Now that we have covered the basic understanding of Diabetes in the previous post, let us now understand the numbers that define normal or impaired diabetic conditions. There are various tests that doctors prescribe to arrive at better assessment of diabetes. However, let us pay close attention to the important blood test parameters which we all need to know for better management of diabetes.
Blood Sugar levels are measured with blood sample. There are 2 sets of tests which help us understand the blood sugar levels in our body. The first test is for understanding these two parameters:
- Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS)
- Post Prandial Blood Sugar (PPBS)
Measuring blood sugar before meals (preferably before eating breakfast) is to get a baseline parameter called “Fasting Blood Sugar” (FBS), and then two hours after meal to measure “Post Prandial Blood Sugar” (PPBS). These two parameters help us understand how well our body is able to manage the blood sugar before and after consuming food. Here is the chart to understand blood sugar levels better in a human body:
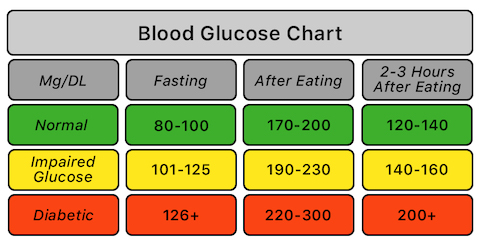
As you can infer from the blood glucose chart here, it is important to ensure our body in in the green zone in both in fasting and after eating phases. While multiple governing health institutions across the globe have a variation of what is mentioned above, think of these numbers as general guidelines. For example, some countries suggest to have after eating PPBS to be between 100-140 for normal range. So, refer to your specific country/region health governing body for the appropriate numbers.
What is HbA1c? Let us understand that a bit more.
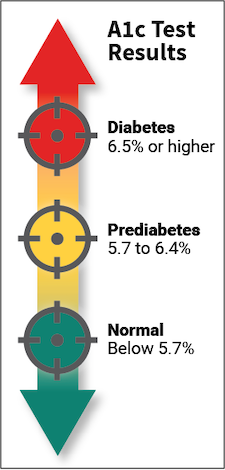
The second key test is to measure “HbA1c“. The hemoglobin A1c test tells the average level of blood sugar over the past 2 to 3 months. It’s also called glycated hemoglobin or glycohemoglobin test.
Let us understand the Normal range for Hemoglobin A1c Test. For people without diabetes, the normal range for the HbA1c level is between 4% and 5.6%. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% mean pre-diabetes condition and indicate a higher chance of getting diabetes. Levels of 6.5% or higher mean a definitive case of diabetes. HbA1c is a kind of gold standard of measure to evaluate the diabetic condition and there by to manage it well given this test provides 3 months average blood glucose levels.
Having known the basics of how to measure and knowing the range of values for FBS, PPBS and HbA1c ascertain the diabetic condition. People with diabetes should have an A1c test every 3 months to make sure their blood sugar is in their target range. If the diabetes is under good control, blood tests can be done for longer periods beyond 3 months. But experts recommend checking at least two times a year. In order to reverse the diabetes or pre-diabetic condition, a combination of diet, exercise, and medication are very important and I plan to cover those aspects in the next post.
Leave a Reply